SSH keys are a secure and convenient way to log in to servers without using a password. This guide explains how to generate an SSH key on a Linux system.
Step 1: Open a Terminal
On your Linux system, open a terminal window (Ctrl + Alt + T). All commands in this guide will be run from there.
Step 2: Generate a New SSH Key Pair
On your terminal, run ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
Replace your_email@example.com with your email address

Step 3: Choose a Save Location
You’ll see a prompt like: Enter file in which to save the key (/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa):
![]()
Press Enter to accept the default location (~/.ssh/id_rsa).
Or type a custom filename to create multiple keys.
Step 4: Add a Passphrase (Optional)
You’ll be asked to set a passphrase:
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):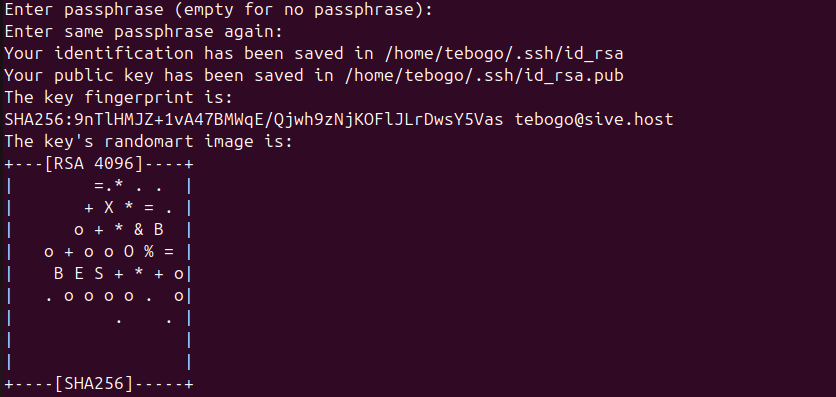
Press Enter for no passphrase (less secure).
Or enter a strong passphrase for extra protection.
After completion, you’ll have:
-
Private key:
~/.ssh/id_rsa(keep safe, never share) -
Public key:
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub(this is the one you share)
Step 5: Display Your Public Key
To view and copy your public key, run: cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
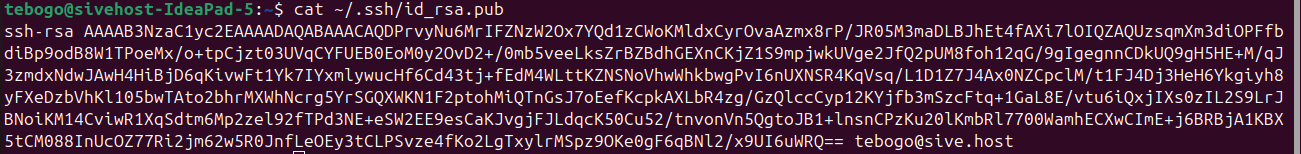
Copy the full key string and paste it where needed


