This tutorial is going to show you how to quickly set up your own email server on Ubuntu 18.04 with Modoboa, which is a free and open-source mail hosting and management platform designed to work with Postfix SMTP server and Dovecot IMAP/POP3 server.
Modoboa is written in Python, released under the terms of ISC license. The latest version is v1.14.0, released on July 5, 2019. Main features of Modoboa are as follows:
- Modoboa by default uses Nginx web server to serve the webmail client and web-based admin panel.
- Compatible with Postfix and Dovecot.
- Support MySQL/MariaDB, or PostgreSQL database.
- Easily create unlimited mailboxes and unlimited mail domains in a web-based admin panel.
- Easily create email alias in the web-based admin panel.
- The webmail client provides an easy-to-use message filter to help you organize messages to different folders.
- It can help you protect your domain reputation by monitoring email blacklists and generating DMARC reports, so your emails have a better chance to land in the inbox instead of the spam folder.
- Includes amavis frontend to block spam and detect viruses in email.
- Calendar and address book.
- Integration with Let’s Encrypt.
- Includes AutoMX to allow end-users to easily configure mail account in a desktop or mobile mail client.
Step 1: Choose the Right Hosting Provider and Buy a Domain Name
To set up a complete email server with Modoboa, you need a server with at least 2GB RAM, because after the installation, your server will use more than 1GB of RAM.
Other VPS providers blocks port 25.
Go to SiveHost website to create an account. Choose the 2GB unmanaged Linux VPS plan.
Once you created an account, Hostwinds will send you an email with the server SSH login details. To log into your server, you use an SSH client. If you are using Linux or MacOS on your computer, then simply open up a terminal window and run the following command to log into your server. Replace 12.34.56.78 with your server’s IP address.
ssh root@12.34.56.78
You will be asked to enter the password. If you are using Windows, please read the following article on how to use SSH client.
You also need a domain name.
Step 2: Creating DNS MX Record
The MX record specifies which host or hosts handle emails for a particular domain name. For example, the host that handles emails for linuxbabe.com is mail.linuxbabe.com. If someone with a Gmail account sends an email to somebody@linuxbabe.com, then Gmail server will query the MX record of linuxbabe.com. When it finds out that mail.linuxbabe.com is responsible for accepting email, it then query the A record of mail.linuxbabe.com to get the IP address, thus the email can be delivered.
In your DNS manager, create a MX record for your domain name. Enter @ in the Name field to represent the main domain name, then enter mail.your-domain.com in the Value field.
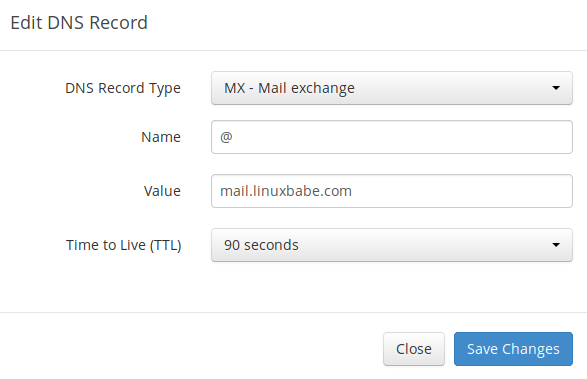
Note: The hostname for MX record can not be an alias to another name. Also, It’s highly recommended that you use hostnames, rather than bare IP addresses for MX record.
Your DNS manager may require you to enter a preference value (aka priority value). It can be any number between 0 and 65,356. A small number has higher priority than a big number. You can enter 0 for your email server, or accept the default value.
After creating MX record, you also need to create an A record for mail.your-domain.com , so that it can be resolved to an IP address. If your server uses IPv6 address, be sure to add AAAA record.
If you uses Cloudflare DNS service, you should not enable the CDN feature when creating A record for your mail server.
Step 3: Set up Mail Server on Ubuntu 18.04 with Modoboa Installer
Log into your server via SSH, then run the following commands to update software packages.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Download modoboa installer from Github.
git clone https://github.com/modoboa/modoboa-installer
Modoboa is written in Python. Run the following command to install the necessary Python software.
sudo apt-get install python-virtualenv python-pip
Then navigate to the modoboa-installer directory and create a configuration file. Replace example.com with your own domain name.
cd modoboa-installer
sudo ./run.py --stop-after-configfile-check example.com
Edit the configuration file installer.cfg with a command line text editor like nano.
sudo nano installer.cfg
To obtain a valid TLS certificate from Let’s Encrypt for your mail server, in [certificate] section, change the value of type from self-signed to letsencrypt.
type = letsencrypt
And change the email address from admin@example.com to your real email address, which will be used for account recovery and important notifications. You will not be able to obtain and install Let’s Encrypt certificate if you use the default email address.

By default, Modoboa installer will install PostgreSQL database server, as indicated by the following lines in the config file.
[database] engine = postgres host = 127.0.0.1 install = true
If you would like to use MariaDB database server, then change the engine from postgres to mysql. (Modoboa will install MariaDB instead of MySQL.)

Save and close the file. (To save a file in Nano text editor, press Ctrl+O, then press Enter to confirm. To exit, press Ctrl+X.)
Next, you should use a fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) as the hostname for your mail server, such as mail.example.com. Run the following command to set the hostname.
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname mail.example.com
Now we need to verify if the DNS records are propagated to the Internet. Depending on the domain registrar you use, your DNS record might be propagated instantly, or it might take up to 24 hours to propagate. You can go to https://dnsmap.io, enter your mail server’s hostname (mail.example.com) to check DNS propagation.
If your DNS record is propagated, run the following command to start the installation.
sudo ./run.py --interactive example.com
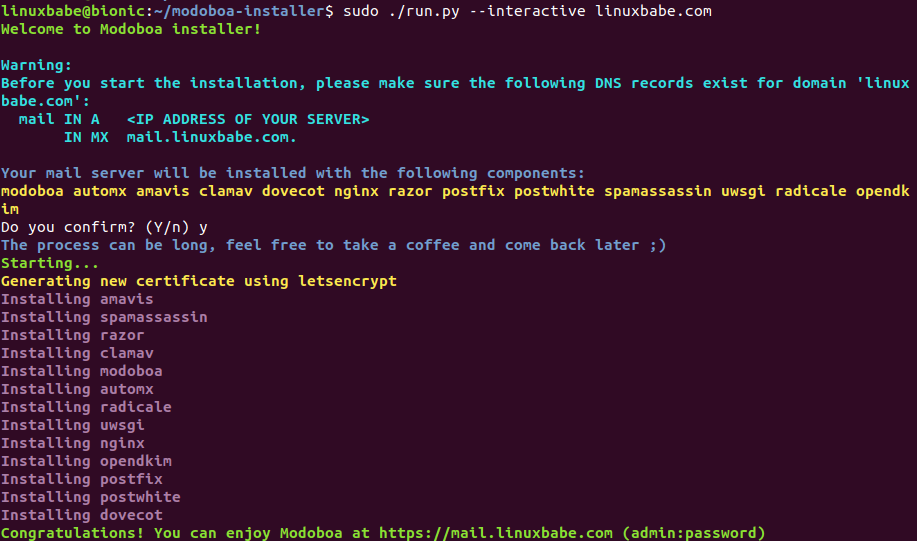
The installation process can take a while. It took 10 minutes on my Hostwinds server. If you see an error during the installation, you can use the --debug option to see more detailed output.
sudo ./run.py --interactive --debug example.com
After Modoboa finishes the installation, you can log into the admin panel with username admin and password password.
Once you are logged in, you should go to Admin -> Settings -> Profile to change the password.
Step 4: Adding Mailboxes in Modoboa Admin Panel
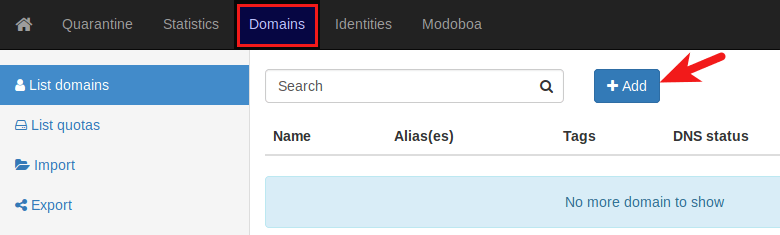
Go to Domains tab and click Add button to add a new domain.
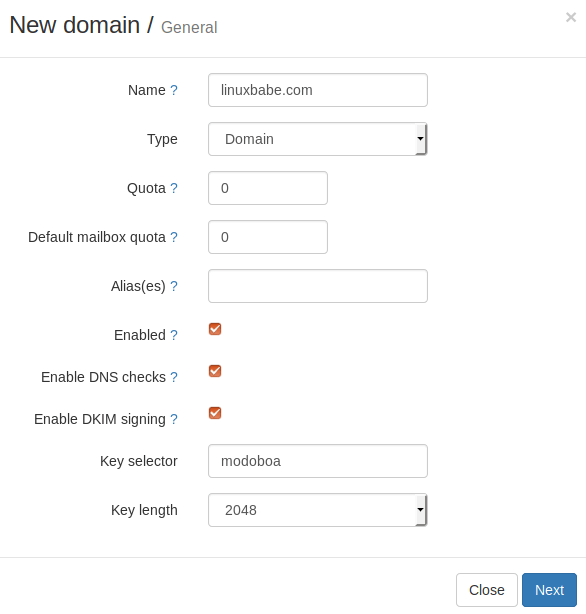
Then enter your main domain name in the Name field. It is highly recommended that you enable DKIM signing, which can help with your domain reputation. In Key selector filed, you can enter a random word like modoboa. Choose 2048 as the key length.
In the next screen, you can choose to create an admin account for your domain. The SMTP protocol requires that a mail server should have a postmaster@example.com address.
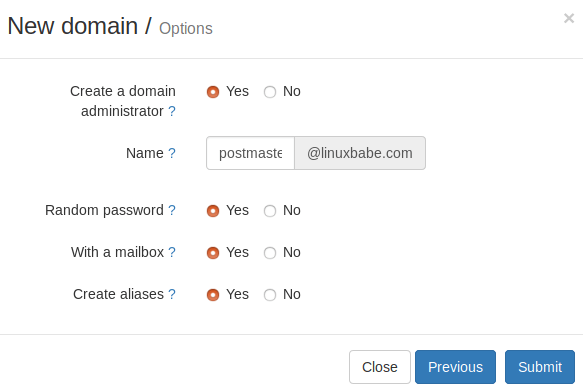
Click the Submit button and your domain name will be added in Modoboa.
To add email addresses, go to Domains tab and click your domain name.
Then click mailboxes.
Click Add button and choose Account.
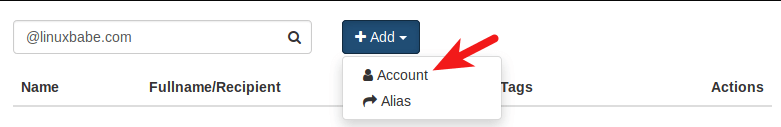
Then choose Simple user as the role. Enter an email address in Username field and enter a password.
In the next screen, you can optionally create an alias for this email address.
After clicking the submit button, the email address is created.
Step 5: Sending Test Emails
To login to the webmail, you need to log out the admin account first and then enter the user credentials.
Once you are logged into Modoboa webmail, you can send a test email from your private email server to your other email address and vice versa.
Inbound emails will be delayed for a few minutes, because by default Modoboa enables greylisting, which tells other sending SMTP server to try again in a few minutes. This is useful to block spam. The following message in /var/log/mail.log indicates greylisting is enabled.
postfix/postscreen[20995]: NOQUEUE: reject: RCPT from [34.209.113.130]:36980: 450 4.3.2 Service currently unavailable;
However, greylisting can be rather annoying. You can disable it by editing the Postfix main configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/postfix/main.cf
Find the following lines at the end of the file and comment them out. (Add a # character at the beginning of each line.)
postscreen_pipelining_enable = yes postscreen_pipelining_action = enforce postscreen_non_smtp_command_enable = yes postscreen_non_smtp_command_action = enforce postscreen_bare_newline_enable = yes postscreen_bare_newline_action = enforce
Save and close the file. Then restart Postfix for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart postfix
Now you should be able to receive emails without waiting several minutes.
Step 6: Checking If Port 25 (outbound) is blocked
Your ISP or hosting provider won’t block incoming connection to port 25 of your server, which means you can receive emails from other mail servers. However, many ISP/hosting providers block outgoing connection to port 25 of other mail servers, which means you can’t send emails.
If your email didn’t arrive at your other email address such as Gmail, then run the following command on your mail server to check if port 25 (outbound) is blocked.
telnet gmail-smtp-in.l.google.com 25
If it’s not blocked, you would see messages like below, which indicates a connection is successfully established. (Hint: Type in quit and press Enter to close the connection.)
Trying 74.125.68.26... Connected to gmail-smtp-in.l.google.com. Escape character is '^]'. 220 mx.google.com ESMTP y22si1641751pll.208 - gsmtp
If port 25 (outbound) is blocked, you would see something like:
Trying 2607:f8b0:400e:c06::1a... Trying 74.125.195.27... telnet: Unable to connect to remote host: Connection timed out
In this case, your Postfix can’t send emails to other SMTP servers. Ask your ISP/hosting provider to open it for you. If they refuse your request, you need to set up SMTP relay to bypass port 25 blocking.
Step 7: Using Mail Clients on Your Computer or Mobile Device
Fire up your desktop email client such as Mozilla Thunderbird and add a mail account.
- In the incoming server section, select IMAP protocol, enter
mail.your-domain.comas the server name, choose port 993 and SSL/TLS. Choosenormal passwordas the authentication method. - In the outgoing section, select SMTP protocol, enter
mail.your-domain.comas the server name, choose port 587 and STARTTLS. Choosenormal passwordas the authentication method.
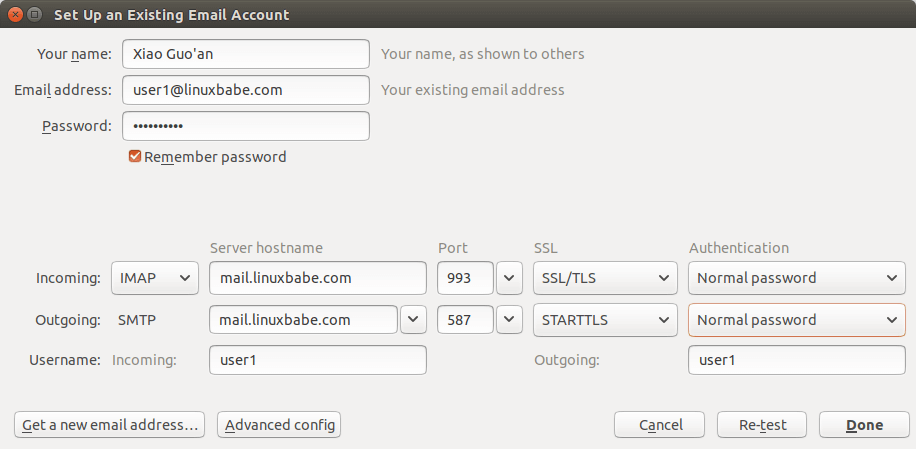
You can also use IMAP on port 143 with STARTTLS encryption.
Step 8: Improving Email Deliverability
To prevent your emails from being flagged as spam, you should set PTR, SPF, DKIM and DMARC records.
PTR record
A pointer record, or PTR record, maps an IP address to a FQDN (fully qualified domain name). It’s the counterpart to the A record and is used for reverse DNS lookup, which can help with blocking spammers. Many SMTP servers reject emails if no PTR record is found for the sending server.
To check the PTR record for an IP address, run this command:
dig -x IP-address +short
or
host IP-address
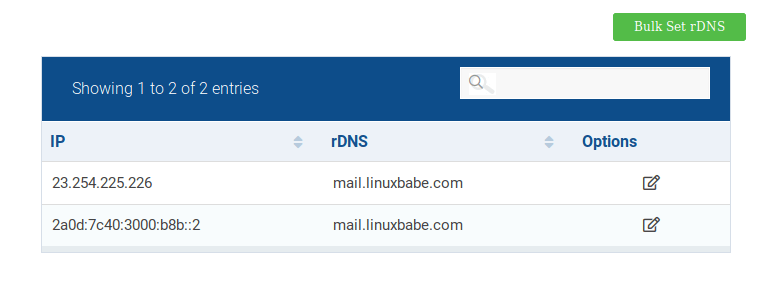
Because you get IP address from your hosting provider or ISP, not from your domain registrar, so you must set PTR record for your IP in the control panel of your hosting provider or ask your ISP. Its value should be your mail server’s hostname: mail.your-domain.com. If your server uses IPv6 address, be sure to add a PTR record for your IPv6 address as well.
To edit the reverse DNS record for your SiveHost VPS, log into Hostwinds client area, select Domains -> Manage rDNS, Then you can edit the reverse DNS record for both IPv4 and IPv6 address.
SPF Record
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record specifies which hosts or IP address are allowed to send emails on behalf of a domain. You should allow only your own email server or your ISP’s server to send emails for your domain. In your DNS management interface, create a new TXT record like below.
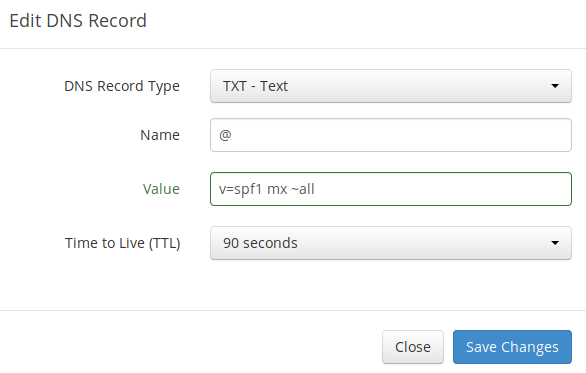
Explanation:
- TXT indicates this is a TXT record.
- Enter @ in the name field to represent the main domain name.
- v=spf1 indicates this is a SPF record and the version is SPF1.
- mx means all hosts listed in the MX records are allowed to send emails for your domain and all other hosts are disallowed.
- ~all indicates that emails from your domain should only come from hosts specified in the SPF record. Emails that are from other hosts will be flagged as forged.
To check if your SPF record is propagated to the public Internet, you can use the dig utility on your Linux machine like below:
dig your-domain.com txt
The txt option tells dig that we only want to query TXT records.
DKIM Record
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) uses a private key to digitally sign emails sent from your domain. Receiving SMTP servers verify the signature by using the public key, which is published in the DNS DKIM record.
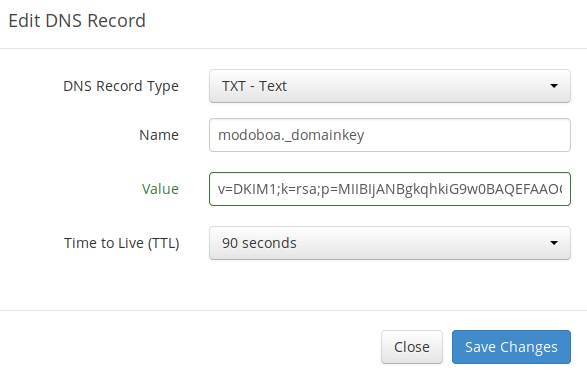
When we were adding domain name in Moboboa admin panel earlier, we enabled DKIM signing, so the signing part is taken care of. The only thing left to do is creating DKIM record in DNS manager. First go to Modoboa admin panel and select your domain name. In the DNS section, click Show key button.
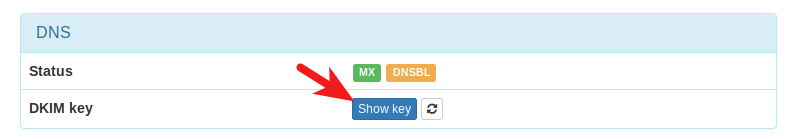
The public key will be revealed. There are two formats. We only need the Bind/named format.
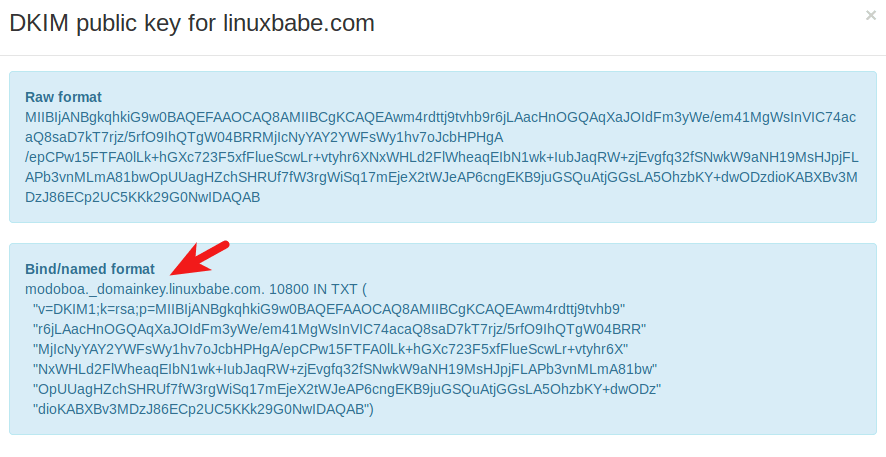 Go to your DNS manager, create a TXT record, enter
Go to your DNS manager, create a TXT record, enter modoboa._domainkey in the Name field. (Recall that we used modoboa as the selector when adding domain name in the admin panel.) Copy everything in the parentheses and paste into the value field. Delete all double quotes. Your DNS manager may require you to delete other invalid characters, such as carriage return.
DMARC Record
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance. DMARC can help receiving email servers to identify legitimate emails and prevent your domain name from being used by email spoofing.
To create a DMARC record, go to your DNS manager and add a TXT record. In the name field, enter _dmarc. In the value field, enter the following:
v=DMARC1; p=none; pct=100; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@your-domain.com
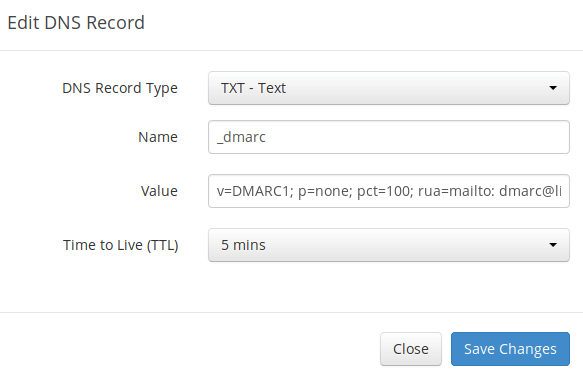
The above DMARC record is a safe starting point.
Step 7: Testing Email Score and Placement
After creating PTR, SPF, DKIM record, go to https://www.mail-tester.com. You will see a unique email address. Send an email from your domain to this address and then check your score. As you can see, I got a perfect score.

Mail-tester.com can only show you a sender score. There’s another service called GlockApps that allow you to check if your email is placed in the recipient’s inbox or spam folder, or rejected outright. It supports many popular email providers like Gmail, Outlook, Hotmail, YahooMail, iCloud mail, etc
What if Your Email is Rejected by Microsoft Mailbox?
Microsoft seems to be using an internal blacklist that blocks many legitimate IP addresses. If your emails are rejected by Outlook or Hotmail, you need to submit the sender information form. After that, your email will be accepted by Outlook/Hotmail.
Auto-Renew Let’s Encrypt TLS Certificate
Modoboa installed the latest version of Let’s Encrypt client (certbot) as /opt/certbot-auto. You can find the location of certbot binary by executing the following command.
sudo find / -name "*certbot*"
Let’s Encrypt TLS certificate is valid for 90 days. To automatically renew the certificate, edit root user’s crontab file.
sudo crontab -e
Add the following line at the end of this file.
@daily /opt/certbot-auto renew -q && systemctl reload nginx postfix dovecot
Save and close the file. This tells Cron to run the certbot renew command every day. If the certificate has 30 days left, certbot will renew it. It’s necessary to reload Nginx web server, Postfix SMTP server and Dovecot IMAP server so they can pick up the new certificate.
Enabling SMTPS Port 465
If you are going to use Microsoft Outlook client, then you need to enable SMTPS port 465 in Postfix SMTP server.
Troubleshooting
First, please use a VPS with at least 2GB RAM. Running Modoboa on a 1GB RAM VPS will cause the database, SpamAssassin, or ClamAV to be killed because of out-of-memory problem. If you really want to use a 1GB RAM VPS, you are going to lose incoming emails and have other undesirable outcomes.
If the Modoboa web interface isn’t accessible, like a 502 gateway error, you should check the Nginx logs in /var/log/nginx/ directory to find clues. You may also want to check the mail log /var/log/mail.log.
Check if the various services are running.
systemctl status postfix systemctl status dovecot systemctl status nginx systemctl status mariadb systemctl status clamav-daemon systemctl status amavis
If you enabled the firewall, you should open the following ports in the firewall.
HTTP port: 80 HTTPS port: 443 SMTP port: 25 Submission port: 587 (and 465 if you are going to use Microsoft Outlook mail client) IMAP port: 143 and 993
I found that the clamav-daemon service has a tendency to stop without clear reason even when there’s enough RAM. This will delay emails for 1 minute. We can configure it to automatically restart if it stops via the systemd service unit. Copy the original service unit file to the /etc/systemd/system/ directory.
sudo cp /lib/systemd/system/clamav-daemon.service /etc/systemd/system/clamav-daemon.service
Then edit the service unit file.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/clamav-daemon.service
Add the following two lines in the [service] section.
Restart=always RestartSec=3
Like this:
[Service] ExecStart=/usr/sbin/clamd --foreground=true # Reload the database ExecReload=/bin/kill -USR2 $MAINPID StandardOutput=syslog Restart=always RestartSec=3
Save and close the file. Then reload systemd and restart clamav-daemon.service.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart clamav-daemon
(Optional) Set Up Autodiscover and AutoConfig to Automate Mail Client Configuration
Autodiscover and AutoConfig make it easy to configure a desktop or mobile mail client. The end


